Electoral Research Abstracts – Segnalazioni bibliografiche
-

What’s new under the sun? A corpus linguistic analysis of the 2022 Italian election campaign themes in party manifestos
To cite the article: Trastulli, F., & Mastroianni, L. (2023). What’s…
-

When institutions matter: electoral systems and intraparty fractionalization in Western Europe
To cite the article: Emanuele, V., Marino, B., and Diodati, N.…
-

The Valence Side of the EU: EU Issue Voting in the Aftermath of the Eurozone Crisis
To cite the article: Carrieri, L., & Angelucci, D. (2021). The Valence Side of…
-

Europe matters … upon closer investigation: a novel approach for analysing individual-level determinants of vote choice across first- and second-order elections, applied to 2019 Italy
Per citare l’articolo: Angelucci, D., De Sio, L., & Paparo, A.…
-
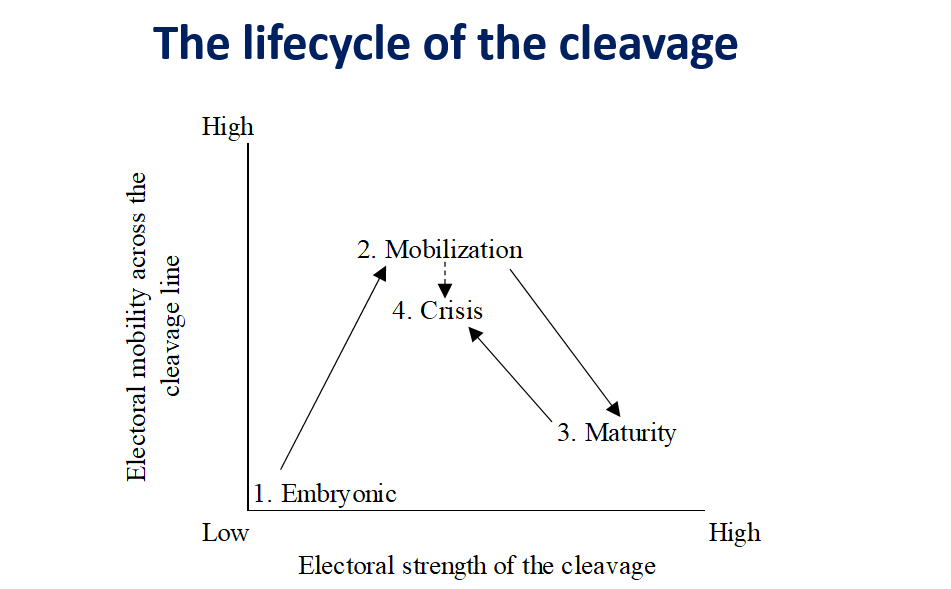
The congealing of a new cleavage? The evolution of the demarcation bloc in Europe (1979–2019)
Per citare l’articolo: Emanuele, V., Marino, B. and Angelucci, D. (2020),…
-
Who’s Favored by Evaluative Voting? An Experiment Conducted During the 2012 French Presidential Election
Abstract Under evaluative voting, the voter freely grades each candidate on…
-
With a little help from my neighbours: A spatial analysis of the impact of local campaigns at the 2010 British general election
Abstract This article examines the electoral impact of spillover effects in…
-
Vote-earning strategies in flexible list systems: Seats at the price of unity
In theory, flexible list systems are a compromise between closed-list and…

