International
-

The hidden cleavage of the French election: Macron, Le Pen and the urban-rural conflict
(traduzione a cura di Elisabetta Mannoni) Notwithstanding Macron’s victory, the result…
-

The 2017 Pd Primaries: Renzi strikes back
(English translation by Elisabetta Mannoni) Matteo Renzi won the primaries of…
-

Conflict mobilization for Le Pen, problem-solving for Macron: voting models reveal two opposite visions of France
(English translation by Elisabetta Mannoni) So Macron and Le Pen get…
-
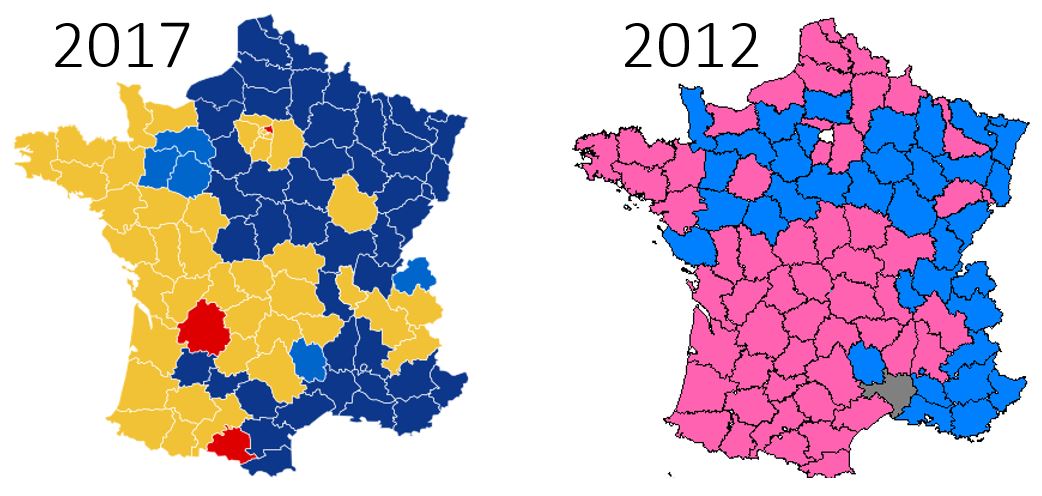
French presidential election: An expected surprise
The eventful and unconventional campaign for the French presidential elections (partly)…
-
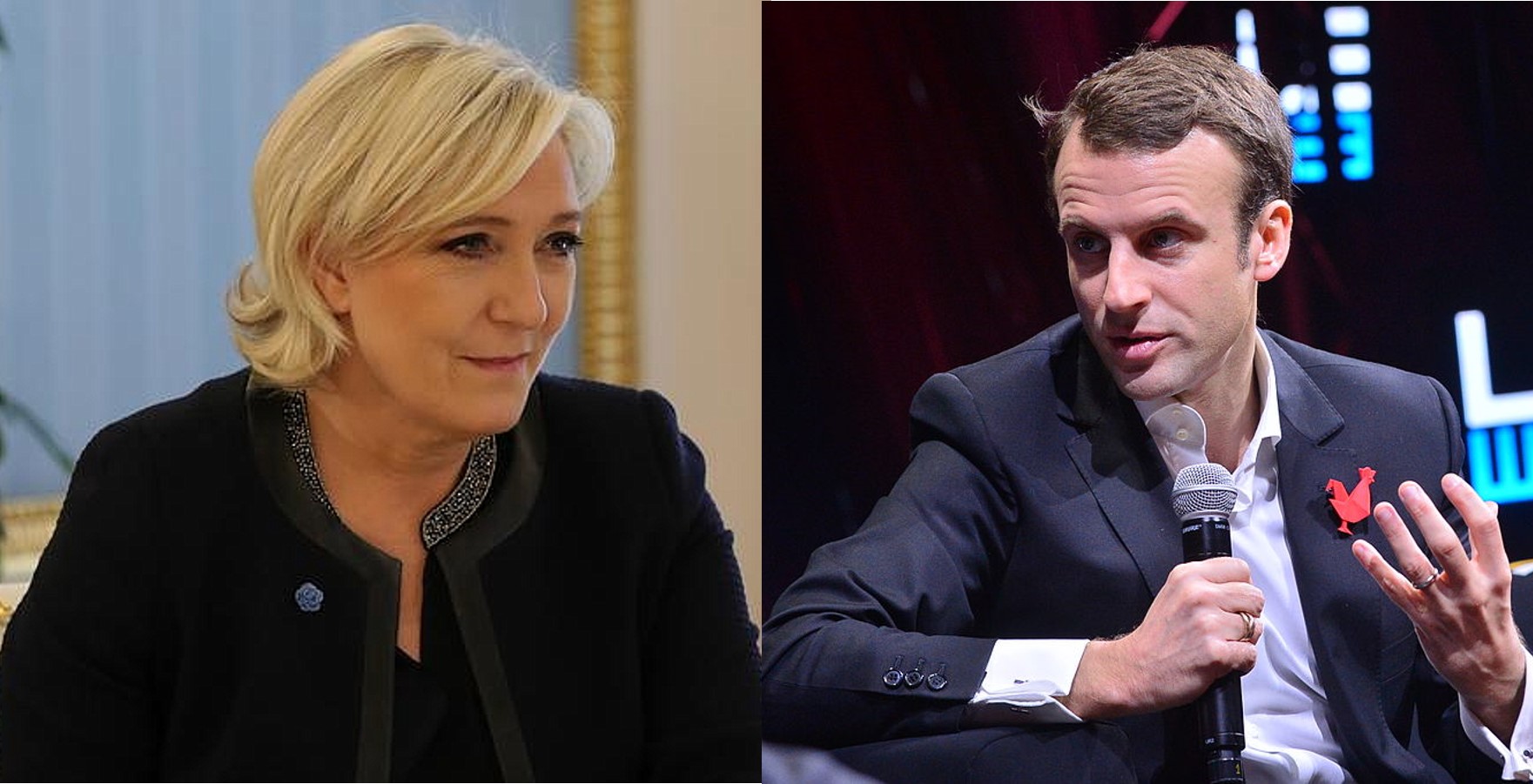

Who will win the Élysée? Figure it out with the CISE online simulator
The long-awaited first round of French presidential election is now history.…
-
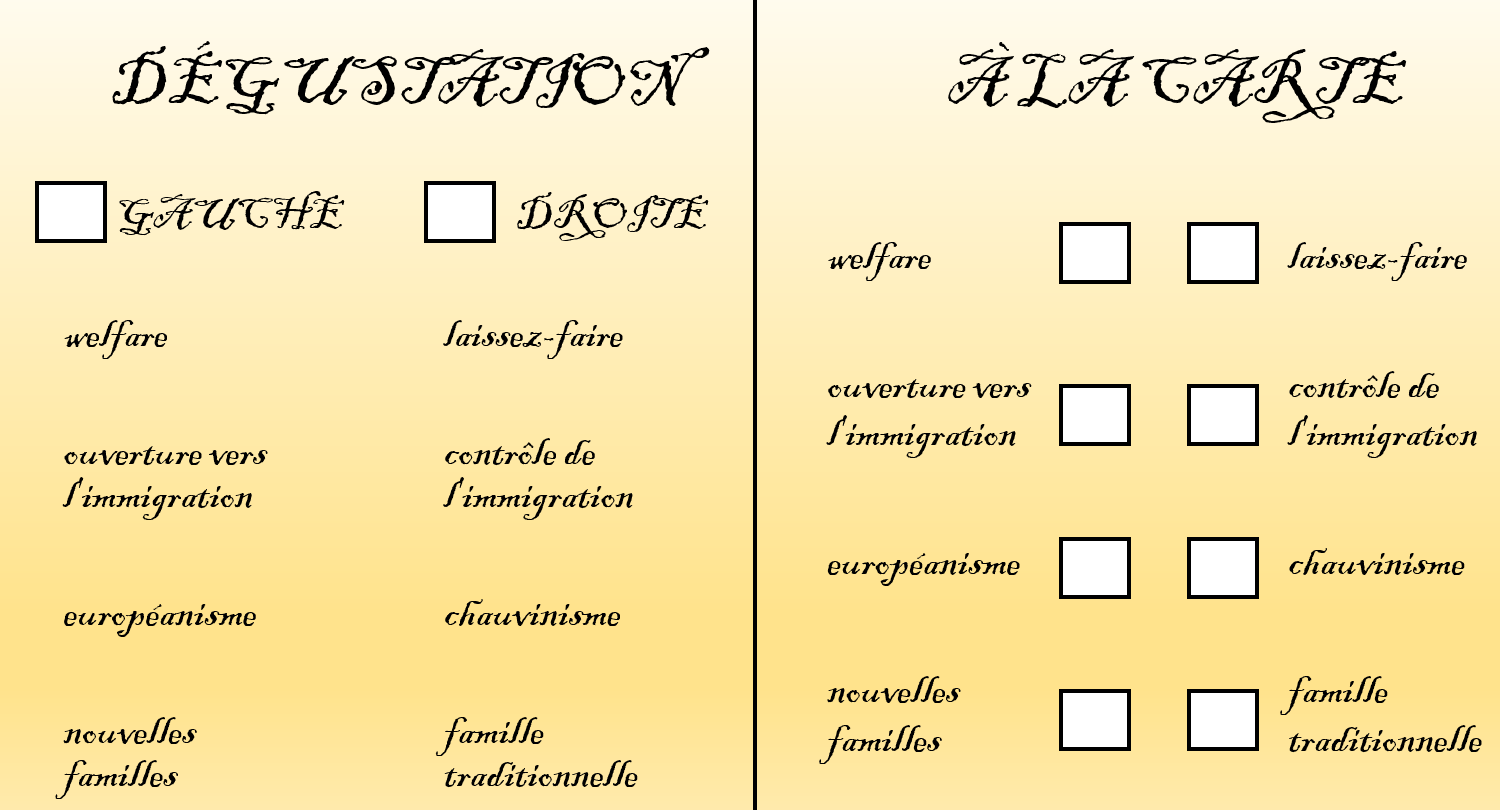
Ideology or ‘cherry-picking’? The issue opportunity structure for candidates in France
Building on the tools provided by issue yield theory (De Sio…
-

Who will solve France’s problems? Candidate credibility on issues with top priority
Next Sunday, French voters will be called to the polls for…
-

A shared agenda, with a right-wing slant: public opinion priorities towards the French Presidential election
As witnessed by the emphasis and the media coverage of pundits…
-

Do citizens identify with a party? A new measurement of party identification tested in Italy
Aldo Paparo & Lorenzo De Sio (2017) PTV gap as a…
-

Party system volatility, regeneration and de-institutionalization in Western Europe (1945–2015)
Chiaramonte, A. and Emanuele, V. (2015), ‘Party System Volatility, Regeneration and…